Change Will Not Stop— in fact, Changes are accelerating more rapidly than ever before. Changes are becoming more disruptive and WE must become more unified and flexible in addressing them head on. Choosing to ignore them and failing to act together, will result in our being overwhelmed with unknown hardships, suffering and certainly repression by those who manipulate changes for selfish motives.
Can we deny this is the harsh reality facing us and our children?
Visible Indicators
In Retrospect Gartner Predicted IP Crime, Super-Organs, and Revolution
Gartner released a report outlined its top predictions for the following six years or so titled “Gartner Top Predictions 2014: Plan for a Disruptive, but Constructive Future”. The report makes some rather startling predictions about the future of our world, often veiled in elliptical phrases reminiscent of the Oracle at Delphi.
Those top predictions focused on disruptions brought about by digital business, the Internet of Things, smart machines and the onset of the Digital Industrial Revolution.
Key Findings
■ Smart machines will both enhance and threaten the ability of employees to do their jobs.
■ 3D printing will create intellectual property rights risks as well as ethical dilemmas about human transplants.
■ Digital business will open new opportunities for businesses to engage customers, employees and partners in a digitally enabled ecosystem.
■ The Internet of Things will bridge the gap between people and computers in ways both subtle and gross.
Strategic Assumptions
The New Industrial Revolution
By 2018, 3D printing will result in the loss of at least $100 billion per year in intellectual property globally.
By 2016, 3D printing of tissues and organs (bioprinting) will cause a global debate about regulating the technology or banning it for both human and nonhuman use.
Digital Business
By 2020, the labor reduction effect of digitalization will cause social unrest and a quest for new economic models in several mature economies.
By 2017, over half of consumer goods manufacturers will employ crowdsourcing to achieve fully 75% of their consumer innovation and R&D capabilities.
By 2017, 80% of consumers will collect, track and barter their personal data for cost savings, convenience and customization.
By 2020, enterprises and governments will fail to protect 75% of sensitive data, and will declassify and grant broad/public access to it.
Smart Machines
By 2024, at least 10% of activities potentially injurious to human life will require mandatory use of a nonoverridable “smart system.”
By 2020, the majority of knowledge worker career paths will be disrupted by smart machines in both positive and negative ways.
By 2017, 10% of computers will be learning rather than processing.
Internet of Things
By 2020, consumer data collected from wearable devices will drive 5% of sales from the Global 1000.
While Gartner also focuses on The Internet of Things, digital business and smart machines in the report, it is 3D printing that makes it relevant to us at 3DPI. According to the report, 3D printing will have a huge impact on intellectual property, saying, “At least one major Western manufacturer will claim to have had intellectual property stolen for a mainstream product by thieves using 3D printers who will likely reside in those same Western markets, rather than in Asia, by 2015,” and, “The global automotive aftermarket parts, toy, IT and consumer product industries will report intellectual property theft worth at least $15 billion in 2016 due to 3D printing.” How to solve such a problem? The report’s author suggests that CEOs take a look at how to prevent forgeries via 3D printing and methods for consumers to ensure the validity of their goods.
The report also determines, with pristine clairvoyance, that bioprinting will become a reality for countries in the Asia/Pacific and an ethical question for Western countries: “And, by 2015, at least one high-profile case of the use of bioprinted organs will become a global headline news story due to its success or failure. That case will most likely be centered on the Asia/Pacific region, with Western countries asking ethical questions related to the case based more on curiosity than fear.” Gartner makes it clear that, by 2016, we will fully understand the implications of 3D bioprinting and that some people will likely have human-animal hybrid organs implanted in them, raising a debate about superhuman organs and the potential for an Island of Dr. Moreau to emerge filled with horrible mistakes of creation (though I may be exaggerating a bit with that last part).
Also tied to the rise in digital manufacturing is the reduction in the number of jobs. Everyone is a robot away from unskilled labour and the Gartner report uses a digital pharmacy to illustrate the point:
Now, imagine a (at this moment, fictional) supply chain in which the patient submits his or her DNA (digitally, based on a blood sample analyzed by a local USB device on a laptop or tablet), and, based on that DNA sample, the pharmaceutical company calculates the appropriate drug — likely leveraging third-party cloud compute capacity and not the local IT department, as this requires massive capacity.
Next, the drug is printed (using an organic or biological 3D printer) — initially at a third party print-shop for biomaterials, but later maybe at the pharmacist or even directly at the patient’s home. Most of today’s unique and critical pharmaceutical processes (requiring massive process rigor and labor), such as batch control, secure label printing and multiyear drug approval processes, become largely irrelevant when pharmaceuticals become one-off digitally designed, produced and administered substances. Similar scenarios can be drawn for media (for example, with virtual or even deceased actors playing CGI roles in virtual plots).
The result of all this is not just a reduction in jobs and a redistribution of wealth from labor to capital or intellectual property, but also a massive reduction in cost and price, leading to many of the “free” offers we now see on the Internet.
The Gartner report makes some bold predictions that, due to the scarcity of jobs and a further redistribution of wealth to the capital class, there will be “A larger-scale version of an Occupy Wall Street-type movement began at the end of 2014, indicating that social unrest is starting to foster political debate.
In 2015, Traditional paid jobs began to be replaced by bartering-based systems and voluntary roles in areas such as patient care,” and that “by 2020, the labor reduction effect of digitalization will cause social unrest and a quest for new economic models in several mature economies.”
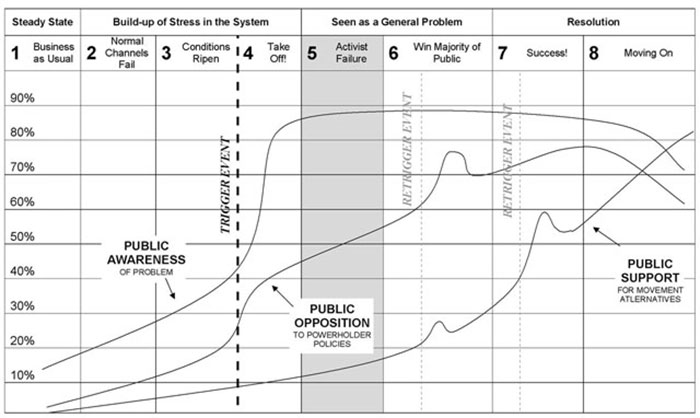
Gartner isn’t the only one to suggest this. If you look at Bill Moyer’s Movement Action Plan model, we may be pretty close to experiencing a social revolution. And take a look at this map that shows a gradual increase in the number of protests across the globe since 1979.
From Bill Moyer’s “The Movement Action Plan”, detailing the historical trends of social movements.
In addition to the strange paradigm shifts caused by 3DP, the Gartner report covers other major technological trends currently at work and where their trajectories lay. Among their visions is the bartering of personal data to companies like Amazon by consumers, the relative opening up of previously classified data to the public by government agencies, computers that operate more through learning than processing, smart machines that will disrupt pretty much every aspect of our lives, and a population of consumers wearing machines that feed all of our personal data to corporations.
Strangely, even though a huge social movement began in 2014, bartering in 2015, and a quest for new economic models by 2020, there will still be companies like Amazon around to collect all of the data from our urine on a daily basis.
(The entire Gartner Report is available below)
Source: Gartner
Gartner Predicted Top 2015 And Beyond Trends For Technology, IT Organizations, And Consumers
On the occasion of its sold-out Symposium/ITxpo this week, Gartner revealed its predictions for top technology trends, the impact of technology on businesses and consumers, and the continuing evolution of the IT organization and the role of the CIO. Here is my summary of Gartner’s press releases:
Digital Disruption Will Give Rise to New Businesses, Some Created by Machines
By 2017, says Gartner, a significant disruptive digital business will be launched that was conceived by a computer algorithm. The most successful startups will mesh the digital world with existing physical logistics to create a consumer-driven network—think Airbnb and Uber—and challenge established markets consisting of isolated physical units.
The meshing of the digital with the physical will impact how we think about product development. By 2015, more than half of traditional consumer products will have native digital extensions and by 2017, 50% of consumer product investments will be redirected to customer experience innovations. The wide availability of product, pricing and customer satisfaction information has eroded the competitive advantage afforded in the past by product innovation and is shifting attention to customer experience innovation as the key to a lasting brand loyalty.
The meshing of the digital with the physical also means the rise of the Internet of Things. “This year,” says Gartner, “enterprises will spend over $40 billion designing, implementing and operating the Internet of Things.” That’s still a tiny slice of worldwide spending on IT which is projected to surpass $3.9 trillion in 2015, a 3.9% increase from 2014. But much of this spending will be driven by the digital economy and the Internet of Things is in the driver seat. Gartner defines digital business as new business designs that blend the virtual world and the physical worlds, changing how processes and industries work through the Internet of Things.
Consider this: Since 2013, 650 million new physical objects have come online; 3D printers became a billion dollar market; 10% of automobiles became connected; and the number of Chief Data Officers and Chief Digital Officer positions have doubled. But fasten your seat belts: In 2015, Gartner predicts, all of these things will double again.
Managing and Leading the Digital Business, Mostly by Humans
Gartner’s survey of 2,800 CIOs in 84 countries showed that CIOs are fully aware that they will need to change in order to succeed in the digital business, with 75% of IT executives saying that they need to change their leadership style in the next three years.
“The exciting news for CIOs,” says Gartner, “is that despite the rise of roles, such as the chief digital officer, they are not doomed to be an observer of the digital revolution.” According the survey, 41% of CIOs are reporting to their CEO. Gartner notes that this is a return to one of the highest levels it has ever been, no doubt because of the increasing importance of information technology to all businesses.
Still, reporting to the CEO does not necessarily mean leading the digital initiatives of the business. Reports from the Symposium highlighted another Gartner finding:
While CIOs say they are driving 47% of digital leadership only 15% of CEOs agree that they do so. Similarly, while CIOs estimate that 79% of IT spending will be “inside” the IT budget (up slightly from last year), Gartner says that 38% of total IT spending is outside of IT already, and predicts that by 2017, it will be over 50%. This is a “shift of demand and control away from IT and toward digital business units closer to the customer,” says Gartner. It further estimates that 50% of all technology sales people are actively selling direct to business units, not IT departments.
Gartner sees the established behaviors and beliefs of the IT organization, the “best practices” that have served it well in previous years, as the biggest obstacle for CIOs in their pursuit of digital leadership. Process management and control our not as important as vision and agility. Compounding the problem of obsolete leadership style and inadequate skills, is a fundamental requirement of the digital business:
It must be unstable. By 2017, 70% of successful digital business models will rely on deliberately unstable processes designed to shift as customer needs shift. “This holistic approach,” says Gartner, “blending business model, processes, technology and people will fuel digital business success.”
The Rise of Smart Machines
By 2015, there will be more than 40 vendors with commercially available managed services offerings leveraging smart machines and industrialized services. By 2018, the total cost of ownership for business operations will bereduced by 30% through smart machines and industrialized services.
Smart machines are an emerging “super class” of technologies that perform a wide variety of work, of both the physical and the intellectual kind. Smart machines will automate decision making. Therefore, they will not only affect jobs based on physical labor, but they will also impact jobs based on complex knowledge worker tasks. “Smart machines,” says Gartner, “will not replace humans as people still need to steer the ship and are critical to interpreting digital outcomes.” But these humans will have new types of jobs.
Top Digital Jobs
By 2018, Gartner predicts, digital business will require 50% less business process workers and 500% more key digital business jobs, compared with traditional models. The top jobs for digital over the next seven years will be:
• Integration Specialists
• Digital Business Architects
• Regulatory Analysts
• Risk Professionals
Gartner: “You must build talent for the digital organization of 2020 now. Not just the digital technology organization, but the whole enterprise. Talent is the key to digital leadership.”
Where Things Can Go Wrong
Gartner highlights two areas of potential vulnerabilities as business pursue digital opportunities: Lack of portfolio management skills and inadequate risk management.
By year-end 2016, 50% of digital transformation initiatives will be unmanageable due to lack of portfolio management skills, leading to a measurable negative lost market share. The digital business brings with it vastly different and higher levels of risk, say 89% of CIOs and 69% believe that the discipline of risk management is not keeping up.
Gartner: “CIOs need to review with the enterprise and IT risk leaders whether risk management is adapting fast enough to a digital world.” This is also an urgent tasks, I might add, for CEOs and the board of directors.
The Pursuit of Longer Life and Increased Happiness (i.e., better shopping experience)
Gartner predicts that all these connected devices will have a positive impact on our health. By 2017, the use of smartphones will reduce by 10% the costs for diabetic care. By 2020, life expectancy in the developed world will increase by 0.5 years due to widespread adoption of wireless health monitoring technology.
The retail industry could be the industry most impacted by the digital tsunami, drastically altering our shopping experience. By year-end 2015, mobile digital assistants will have taken on tactical mundane processes such as filling out names, addresses and credit card information. By year-end 2016, more than $2 billion in online shopping will be performed exclusively by mobile digital assistants. Yearly autonomous mobile assistant purchasing will reach $2 billion dollars annually, representing about 2.5 percent of mobile users trusting assistants with $50 a year.
By 2017, U.S. customers’ mobile engagement behavior will drive mobile commerce revenue in the U.S. to 50% of U.S. digital commerce revenue. A renewed interest in mobile payments will arise in 2015, together with a significant increase in mobile commerce. By 2016, there will be an increase in the number of offers from retailers focused on customer location and the length of time in store. By 2020, retail businesses that utilize targeted messaging in combination with internal positioning systems (IPS) will see a five percent increase in sales.
These trends seem to be a logical extension of current technologies. But 3D printing will bring us a completely new shopping experience and will expand widely what’s on offer. By 2015, more than 90% of online retailers of durable goods will actively seek external partnerships to support the new “personalized” product business models and by 2017, nearly 20% of these retailers will use 3D printing to create personalized product offerings.
Gartner: “The companies that set the strategy early will end up defining the space within their categories.”
This statement, which Gartner made specifically about the personalized products business, is true for all types of digital businesses and for all the new management processes and attitudes that all organizations should put in place, sooner rather than later.
Sources:
Gartner Reveals Top Predictions for IT Organizations and Users for 2015 and Beyond
Gartner Identifies the Top 10 Strategic Technology Trends for 2015